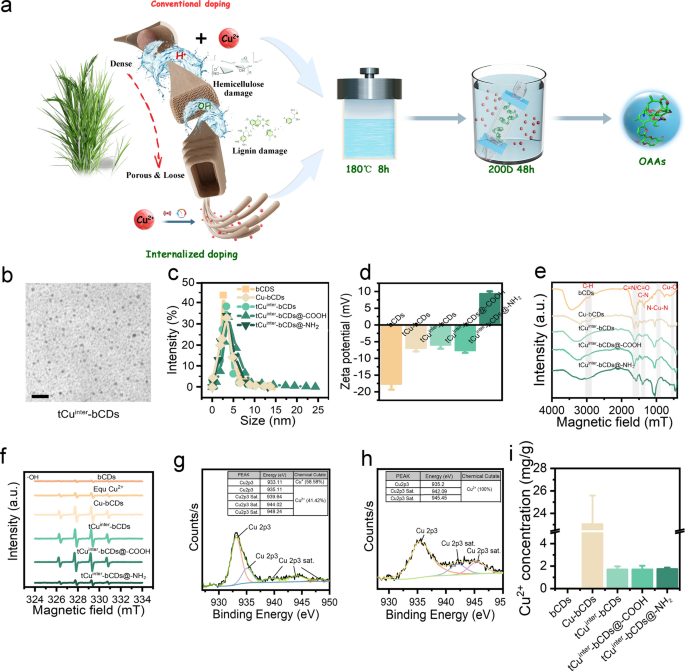
Establishing inexperienced and environment friendly OAAs based mostly on copper internalization
Utilizing agricultural waste biomass straw as a carbon supply, completely different doping schemes and modification strategies have been employed to organize numerous varieties of OAAs (Fig. 1a), together with bCDs, Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH, and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2. Characterization of bCDs, Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, and their surface-modified counterparts is illustrated in Fig. 1. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirmed the morphological options of bCDs, Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH, and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2, with a median particle measurement distribution starting from 2.90 to 4.51 nm (Fig. 1b, c, S1). Potential measurements indicated bCDs had a possible of − 17.67 mV, whereas Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH confirmed adverse potentials of − 6.94 mV, − 5.97 mV, and − 7.65 mV, respectively, tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 displayed a optimistic potential of + 9.37 mV (Fig. 1d). Fourier remodel infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) evaluation confirmed copper doping and useful group modifications (Fig. 1e), with peaks at 2943 cm−1 attributed to C–H stretching vibrations, and people at 1634 cm−1 to C=O/C=N stretching vibrations. C–C and C–N stretching vibrations have been noticed at 1660 cm−1 and 1348 cm−1, respectively. Peaks between 900 cm−1 and 1100 cm−1 have been attributed to N–Cu–N stretching vibrations, and the height at 531 cm−1 to Cu–O vibrations, indicating profitable copper doping [30].
OAAs synthesis and characterization. a Schematic illustration depicting typical copper ion doping and internalized doping synthesis. b Transmission electron microscope (TEM) photographs show tCuinter-bCDs, the dimensions bar represents 20 nm. c–e Particle measurement, electrochemical potential, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses are offered for OAAs synthesized by way of numerous schemes and modifications. f. Hydroxyl radicals (·OH) induction ranges in numerous supplies are proven. g–h Cu 2p scans of tCuinter-bCDs and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2, performed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), are depicted. i. Copper ion content material in OAAs is documented
The environment friendly induction of radicals is essential for the degradation of plant viruses. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) exams have been carried out to research the yields of oxygen radicals (O2·−) (Determine S2a), singlet oxygen (1O2) (Determine S2b), and hydroxyl radicals (·OH) (Fig. 1f). Outcomes confirmed that the technology of 1O2 throughout OAAs remedy was comparatively low. Nonetheless, Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCD, and tCuinter-bCD@-COOH exhibited greater ranges of O2·− and ·OH manufacturing, with comparable quantities. This means that these OAAs possess enhanced capabilities to induce oxidative stress. Quite a few research have demonstrated that O2·− radicals, produced as byproducts of photocatalytic reactions by way of vitality switch [31,32,33], don’t take part in peptide hydrolysis, whereas ·OH is understood for its protein-cleaving skills [34]. Thus, the first mechanism for protein degradation seems to be the induction of ·OH by OAAs, whereas the contributions of 1O2 and O2·− are minimal. Consequently, tCuinter-bCDs and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH have emerged as the best OAAs for protein degradation.
To additional elucidate the basic valence state composition of OAAs modified with completely different fees, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) evaluation was performed. The complete XPS spectra of tCuinter-bCDs and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 revealed three distinct peaks at 284.1 eV, 531.0 eV, and 933.4 eV (Determine S3a), equivalent to C 1 s, O 1 s, and Cu 2p, respectively. bCDs exhibited solely two peaks, equivalent to C 1 s and O 1 s (Determine S3a, b). Additional high-resolution XPS evaluation of the C 1 s band in tCuinter-bCDs and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 revealed three distinct peaks at 284.8 eV, 286.3 eV, and 288.2 eV, attributed to C–C/C–H, C–O/C–N, and C = O bonds, respectively (Determine S3c). The O 1 s spectrum exhibited two peaks at 531.6 eV, 533.0 eV, equivalent to C=O, C–O bonds, respectively (Determine S3d). Notably, the detailed Cu 2p spectra of tCuinter-bCDs revealed peaks at 933.1 eV, 935.1 eV, 939.6 eV, 944.0 eV, and 948.2 eV, representing Cu 2p3 and Cu 2p3 Sat., indicating the coexistence of Cu+ and Cu2+, with contents of 58.58% and 41.42%, respectively (Fig. 1g). In distinction, the Cu 2p spectra of tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 revealed peaks solely at 935.2 eV, 942.1 eV, and 945.5 eV, indicating the presence of Cu2+ (Fig. 1h). Cu2+ can provoke ·OH manufacturing by way of a Fenton-like response. Nonetheless, the ratio of Cu2+ to Cu+ determines their exercise and longevity, which may activate H2O2 to provide ROS because of the twin roles of H2O2 as a reductant and an oxidant [35, 36]. The conversion and recycling of valence states of multivalent metals are essential within the manufacturing of ROS and the degradation of natural contaminants [37].
Lastly, Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) was employed to find out the Cu concentrations in OAAs (Fig. 1i). The outcomes indicated that typical copper doping ranges considerably exceeded these of hint internalized doping, with a median focus 13.5 instances higher than that of tCuinter-bCDs. Biomass-mediated internalized doping reduces the copper ion content material in OAAs, possible because of the removing of extraneous copper ions throughout synthesis. Regardless of decreased doping, useful exercise stays unaffected, whereas concurrently enhancing materials biocompatibility and environmental friendliness.
OAAs with adverse fees exhibit extremely environment friendly antiviral exercise in plant
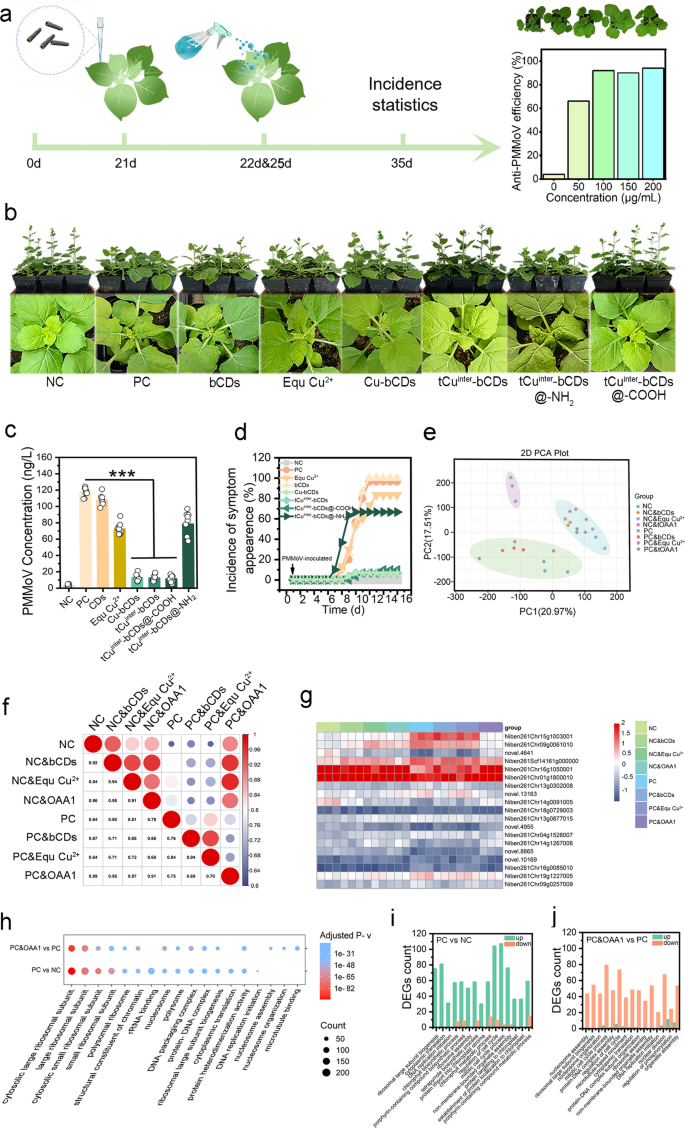
Based mostly on the PMMoV pDNA vector, a tobacco an infection mannequin was established, and virus-exposed or unexposed leaves have been handled with completely different concentrations of tCuinter-bCDs (Fig. 2a, Determine S6a–c), outcomes confirmed {that a} focus of 100 μg ml−1 was the very best anti-plant virus routine. At this focus, the anti-plant virus effectivity of various OAA was verified (Fig. 2b), Antiviral efficacy was assessed by analyzing plant physiological and progress parameters and quantitatively evaluating virus ranges by way of the detection of virus rely and virus-related gene expression. Biomass evaluation revealed that the adverse management (NC), Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH remedy teams displayed comparable lots (averaging 9.84–10.96 g), whereas the optimistic management (PC), bCDs, EquCu2+, and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 teams exhibited decrease ranges (averaging 6.65–7.28 g), with the previous considerably greater than the latter (Determine S4a). Plant top and the variety of leaves per plant (PCS) confirmed the same development, with the NC, Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH remedies leading to heights of two.21, 1.88, 1.97, and a pair of.01 instances and PCS of 1.57, 1.48, 1.65, and 1.65 instances these of the PC, respectively (Figures S4, S5). Statistical evaluation of the incidence price over time beneath PMMoV inoculation and OAAs publicity revealed symptom manifestation across the seventh day with out efficient OAA intervention, as evidenced by the outcomes of the PC (Fig. 2c). EquCu2+ and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 displayed low effectivity in resisting PMMoV, with efficiencies of solely 16.67% and 33.33%, respectively, adopted by the Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH publicity teams, with efficiencies of 93.33%, 93.33%, and 90%, respectively. To exactly quantify the buildup stage of virus particles in plant tissues, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was employed (Fig. 2d). The outcomes indicated that Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs, and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH remedies led to minimal virus publicity, decreasing virus ranges by 88.94%, 88.29%, and 84.20%, respectively, in comparison with PC. Whereas EquCu2+ and tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 exhibited a major lower in virus content material in comparison with PC. This reveals that when thought-about alongside physiological and progress parameters, they fell in need of environment friendly virus prevention and management. TEM imaging of the virus within the plant tissue fluid from each the PC and tCuinter-bCDs remedy teams supplied extra verification of the beforehand talked about findings (Determine S7).
Depicts the evaluation of antiviral exercise in stay crops towards PMMoV utilizing numerous supplies. a The scheme illustrated the timeline of PMMoV inoculate and tCuinter-bCDs remedy. b Morphological modifications and signs in Nicotiana benthamiana have been o bserved post-inoculation with PMMoV (PC) and in comparison with non-inoculated controls (NC); pictures have been taken at 36 days post-inoculation (dpi). c PMMoV content material was decided through ELISA, with samples collected 16 days post-inoculation, together with 3 organic and three technical replicates per remedy. d The kinetics of symptom improvement following PMMoV inoculation have been statistically analyzed over a 16-day interval, ranging from the day of inoculation, with 30 crops per remedy. e PCA evaluation of the DEGs. f Correlation evaluation of the FPKM for DEGs in crops uncovered to antiviral brokers both inoculated with PMMoV or not. g Heatmap evaluation of DEGs associated to virus proliferation-induced protein expression and plant virus protection, annotated with GO-enriched phrases for expression-related genes. h Comparability of the enriched GO phrases between PC vs. NC and PC & OAA1 vs. PC, specializing in the highest 15 considerably enriched phrases. i, j Statistics of the upregulated and downregulated expression ranges of DEGs among the many prime 15 considerably enriched GO phrases in PC vs. NC and PC & OAA1 vs. PC.
PMMoV includes ORF1 (126 kDa) with methyltransferase and helicase exercise, and ORF2 (183 kDa) with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase exercise. Along with the motion protein (MP, ORF3) and capsid protein (CP, ORF4), they represent the construction of PMMoV. All 4 proteins are indispensable for PMMoV’s replication and meeting. To additional assess the potential threat of virus proliferation, the expression ranges of those 4 protein genes in leaves uncovered to the management teams (NC, PC) and tCuinter-bCDs have been examined utilizing qPCR (Figures S8a–d, S9a–e). The outcomes revealed the absence of ORF1, ORF2, and CP in each NC and tCuinter-bCDs, and MP confirmed minimal expression. Nonetheless, its presence alone doesn’t pose a menace to PMMoV’s meeting and proliferation. Based mostly on these findings, the extremely efficient in vivo anti-PMMoV exercise of Cu-bCDs, tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH, and tCuinter-bCDs was validated.
Following plant virus an infection, the viral genetic materials was built-in into the plant’s genome, selling the expression of pathways associated to plant protein synthesis to facilitate speedy proliferation [38, 39]. This course of intensifies the plant’s metabolic burden, resulting in progress aberrations corresponding to leaf curling, decreased stature, and decreased biomass [40]. Our examine comprehensively assessed each progress phenotypes and physiological parameters, revealing the outstanding efficacy of OAAs towards PMMoV. Notably, tCuinter-bCDs@-NH2 and tCuinter-bCDs@-COOH displayed notable distinctions in vivo antiviral efficacy, possible stemming from variations in copper ions with distinct valence states; that is immediately associated to the induction effectivity of free radicals. Furthermore, conventionally synthesized Cu-bCDs demonstrated comparable antiviral effectivity to tCuinter-bCDs however leached greater ambient copper ranges. Consequently, as a consequence of their facile synthesis and eco-friendliness, additional exploration into the anti-plant virus exercise and mechanism of tCuinter-bCDs (OAA1) was carried out.
To validate the outstanding efficacy of OAA1 in enhancing photosynthesis, an evaluation of the photosynthetic response effectivity to various ranges of CO2 (0–1800 μmol m−2 s−1) and lightweight (0–1800 μmol m−2 s−1) was performed (Determine S10a, b). Below stress from PMMoV an infection, the photosynthetic capability skilled a noticeable decline within the PC group in each response curves. Regardless of its recognized antiviral properties, EquCu2+ failed to totally restore photosynthetic effectivity to regular ranges. Intriguingly, whereas preliminary levels of bCDs remedy didn’t exhibit clear antiviral results, they remarkably preserved regular photosynthetic ranges in PMMoV-infected crops. In the meantime, the OAA1 remedy showcased twin performance, successfully combating PMMoV whereas concurrently enhancing photosynthesis, which can enhances photosynthetic effectivity primarily by functioning as an electron transport service, enhancing the effectivity of photonic-electronic conversion and thus enhancing photosynthetic effectivity. Analyzing the sunshine response curve, a decline in photosynthetic effectivity beneath excessive gentle depth was noticed, probably because of the phototoxic results of bCDs fluorescence. Additional assessments beneath pure circumstances (CO2 400 μmol mol−1, PAR 1000 μmol−2 s−1) confirmed that PMMoV-infected crops handled with OAA1 exhibited noteworthy enhancements in internet photosynthetic price (Pn) (Determine S11a), stomatal conductance (Gs) (Determine S11c), and transpiration price (E) (Determine S11d), with will increase of 62.00%, 58.68%, and 53.47% respectively in comparison with PC, and the publicity to bCDs notably improved (17.53%) the Pn. Furthermore, publicity to each bCDs and OAA1 considerably elevated chlorophyll ranges (together with chlorophyll a and b), whereas carotenoid ranges remained unchanged.
(Determine S12a–d). The correlation between improved photosynthesis and nitrogen ranges was additional confirmed by way of whole nitrogen content material evaluation (Determine S13).
Quite a few research have confirmed that salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) are essential secondary metabolites in combating plant viruses, with their biosynthesis intricately linked to chloroplasts [38, 41, 42]. Plant viruses disrupt hormone synthesis by focusing on chloroplasts to facilitate an infection [43], resulting in signs corresponding to leaf chlorosis and mottling. Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), Tomato mosaic virus (ToMV) [44, 45], Rice stripe virus (RSV) [46], and Potato virus X (PVX) [47] have all demonstrated injury to the host photosynthetic methods. On this examine, useful OAA1 and bCDs supplies have been utilized to mitigate the chlorophyll stress brought on by plant viruses, thereby selling the manufacturing of plant hormones with immune exercise to successfully fight towards viral infections.
Transcriptional evaluation elucidates the molecular response of OAA1 towards PMMoV
Transcriptomic evaluation revealed the host response to plant viruses, demonstrating that crops have advanced advanced protection mechanisms towards viruses, together with immune receptor signaling, RNA silencing, hormone-mediated protection pathways, and protein degradation [48]. Preliminary experiments have proven that OAA1 can successfully inhibit plant virus invasion and improve photosynthesis. To elucidate the expression of associated genes throughout the interplay between plant viruses and crops, transcriptomic evaluation was performed on tobacco leaves contaminated with PMMoV for 7 days and handled with completely different supplies as controls. PCA clustering outcomes indicated that the NC, with none remedy, was categorized individually. Ineffective remedy teams for virus an infection, corresponding to PC, PC&bCDs, and PC&EquCu2+, clustered collectively. NC&bCDs, NC&EquCu2+, NC&OAA1, and PC&OAA1 additionally clustered collectively, indicating a wholesome plant response to nanomaterials. Notably, PC&OAA1, as a remedy group for virus an infection, clustered with this group, suggesting that the plant viruses have been effectively inhibited by OAA1 (Fig. 2e). PC generated numerous differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in comparison with NC (Determine S14a). Nonetheless, publicity to OAA1 considerably decreased the extent of DEGs in PC, indicating the therapeutic impact of OAA1 towards PMMoV (Figures S14b, c, S15). Correlation evaluation of FPKM values confirmed that PC&OAA1 demonstrated sturdy correlations with NC, NC&bCDs, NC&EquCu2+, and NC&OAA1, yielding correlation coefficients of 0.89, 0.95, 0.97, and 0.91, respectively (Fig. 2f).
Within the absence of PMMoV inoculation, publicity to bCDs and OAA1 considerably upregulates the expression of genes associated to photosynthesis (Determine S16a, b). This discovering aligns with the outcomes of prior research on gentle and parameter detection. Among the many prime 15 GO enriched pathways for NC&bCDs vs. NC, 9 are related to photosynthesis or the synthesis and metabolism of photosynthetic pigments, whereas for OAA1, there are 8 such pathways, with almost all related genes noticed to be upregulated (Determine S17a, b). Nonetheless, when inoculated with PMMoV, remedy with bCDs alone doesn’t result in important enrichment of pathways associated to photosynthesis, as an alternative primarily enriching in antiviral secondary metabolites corresponding to salicylic acid synthesis and metabolism, and antioxidant features. Due to this fact, it’s speculated that the composite doping of bCDs with copper reveals twin features in selling photosynthesis and resistance to PMMoV.
An infection by plant viruses triggers the considerably upregulation of genes related to ribosome meeting and protein synthesis (Fig. 2h), thereby accelerating the method of virus replication and meeting. Among the many prime 15 GO enriched phrases for differentially expressed genes between the PC and NC teams, 14 are associated to ribosome meeting and protein synthesis. Therapy with OAA1 results in a noticeable downregulation within the expression of genes associated to ribosome meeting and protein synthesis (Fig. 2i, j), with 13 out of the highest 15 GO enriched phrases for DEGs indicating protein transcription and ribosome meeting features. These outcomes additional affirm the efficient intervention of OAA1 within the replication and proliferation of PMMoV on the molecular biology stage.
Kmeans clustering of DEGs produced eight distinct gene clusters, Courses 1–8, containing 5669, 6226, 6178, 5981, 5509, 6721, 7093, and 7640 DEGs, respectively (Determine S18). Cluster 3 primarily exhibited important results following publicity to bCDs and EquCu2+ after PMMoV an infection. Clusters1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 have been primarily influenced by each OAAs and PMMoV an infection. Clusters 7 and eight have been primarily influenced by OAA1 publicity. Cluster 7 confirmed downregulation of gene expression induced by PMMoV an infection, indicative of plant useful injury brought on by PMMoV stress. Nonetheless, publicity to OAA1 might reverse this impact, restoring gene expression to regular ranges. Cluster 8 confirmed upregulation of gene expression induced by PMMoV an infection, which can symbolize a cluster of protection genes induced by PMMoV. Publicity to OAA1 might induce these genes to return to regular ranges, suggesting a virus protection operate of OAA1.
Additional gene expression evaluation revealed that, in comparison with the NC group, NC&OAAs teams, and PC&OAA1, different PC&OAAs teams exhibited considerably elevated expression of antiviral protection mechanisms (Fig. 2g). Of the 19 genes related to plant virus protection examined, 14 confirmed notable upregulation. Such upregulation is essentially the most direct proof of viral intrusion [49]. Each the PC&OAA1 and NC&OAAs teams maintained low expression ranges just like these of the NC group, thus confirming the antiviral efficacy of OAA1. The genes related to photosynthesis have been upregulated when uncovered to OAAs (NC&bCDs, NC&OAA1, PC&bCDs, PC&OAA1) compared to NC (Determine S19). Moreover, evaluation of 385 genes concerned in protein transcription, translation, and ribosome meeting revealed a constant expression sample with these associated to antiviral protection (Determine S20). PC, PC&bCDs, and PC&EquCu2+ displayed elevated expression ranges, with PC displaying essentially the most marked improve. Genes related to ribosome meeting and protein expression in crops have been considerably downregulated beneath OAA1 publicity, indicating a molecular response following viral clearance. Furthermore, research have proven that WUSCHEL inhibits viral protein synthesis by suppressing the expression of plant S-adenosyl-l-methionine-dependent methyltransferases concerned in ribosomal RNA processing and ribosome stability [39]. Though their processes are reverse, they’re adequate to exhibit the suppression of plant viruses inside tissues. qRT-PCR evaluation of chosen genes (associated to photosynthesis and protein expression) with stage-specific expression patterns additional helps these findings, aligning with the transcriptomic outcomes (Determine S21a, b).
OAA1 synergistically with exogenous H2O2 allow environment friendly degradation of CP and PMMoV
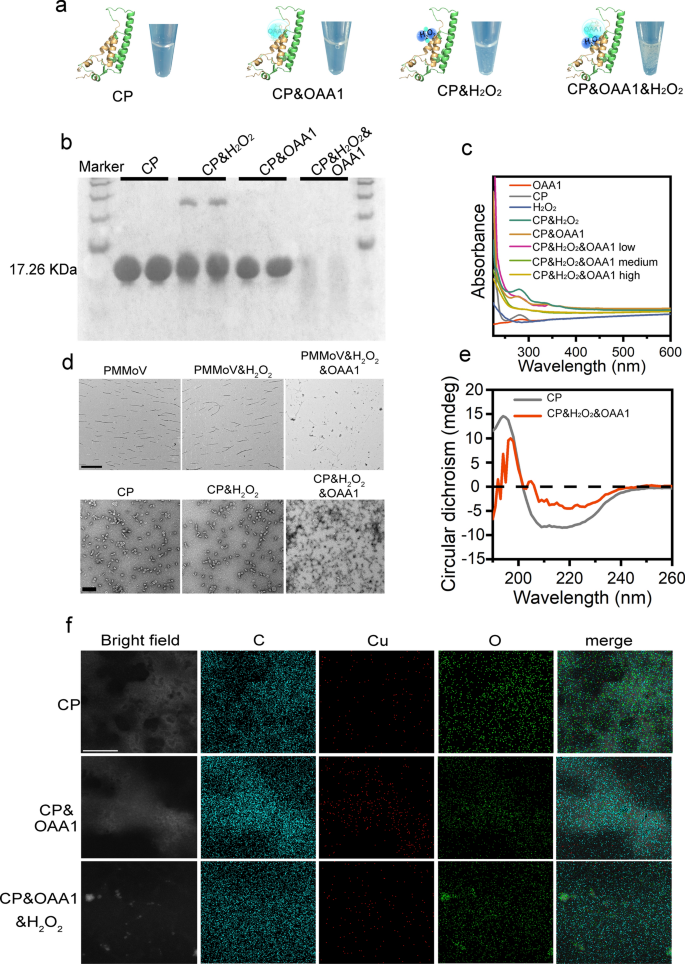
To validate the degradation mechanism of OAA1 towards PMMoV, in vitro degradation experiments have been performed utilizing purified coat protein (CP) expressed from plasmids and PMMoV remoted from plant purification. First, SDS-PAGE evaluation (Determine S22) recognized a 17.26 kDa CP in each contaminated plant tissue and purified expression merchandise [50]. The degradation experiments confirmed the degradation of CP or PMMoV beneath numerous circumstances, revealing a major hyperlink between CP or PMMoV degradation and the incorporation of H2O2 (Fig. 3a, b, Determine S23). OAAs with a adverse cost exhibited greater degradation effectivity in comparison with these with a optimistic cost, and the addition of H2O2 was essential for activating this degradation (Determine S24). The degradation effectivity of CP was assessed at completely different ratios of OAA1 and H2O2. Outcomes indicated {that a} low focus of OAA1 and H2O2 couldn’t fully break down CP aggregates, and degradation initiation occurred at ratios of OAA1 and H2O2 (30%) equivalent to 1 μl and three μl in a 100 μl CP resolution, reaching optimum degradation effectivity when elevated concurrently to five μl (Figures S25, 26). Earlier analysis has proven that pH and ion focus considerably affect the self-assembly of rod-shaped virus proteins [51]. Due to this fact, degradation exercise was verified throughout a pH vary of 4–9. It was discovered that CP degradation was minimally affected solely at pH 4, whereas degradation at different pH ranges was almost full (Determine S27). No important variations have been noticed when it comes to ion focus (NaCl 0.2–1 mM) (Determine S28).
Evaluation of the degradation effectivity of OAA1 on CP. a The schematic illustration of CP inactivation by OAA1, H2O2 or OAA1/H2O2. bValidation of the circumstances for OAA1 and H2O2 remedy on CP degradation was carried out utilizing SDS-PAGE protein gel electrophoresis. Every remedy was independently repeated twice, with an incubation time of 5 min. c UV–seen spectroscopic evaluation of CP degradation, the place low = 0.1 μl, medium = 5 μl, and excessive = 10 μl. d TEM photographs of PMMoV virus particles and CP degradation, PMMoV scale bar = 1 μm, CP scale bar = 100 nm. e Round dichroism evaluation of variations in CP secondary construction earlier than and after degradation. f Co-localization evaluation of attribute components C, Cu, and O earlier than and after degradation with CP or residual degradation fragments, scale bar = 100 nm
UV spectroscopy evaluation detected a major absorption peak for CP at 280 nm [52], which notably diminished beneath the mixed affect of OAA1 and H2O2, indicating efficient degradation (Fig. 3c). Round dichroism (CD) evaluation revealed substantial alterations in CP’s secondary construction post-treatment [53] (Fig. 3e). The share of helices decreased from 99.50% to 85.30%, antiparallel constructions marginally rose from 0 to 0.20%, parallel constructions elevated from 0.20% to 2.40%, beta-turns from 3.30% to 11.70%, and random coils from 0.30% to 2.00% (Desk S1). TEM evaluation of the degradation course of for PMMoV and CP confirmed that OAA1, when mixed with H2O2, successfully fragmented the virus particles and CP fragments (Fig. 3d). Total, the outcomes recommend that OAA1 facilitates virus disintegration by synergistically producing potent ROS with H2O2, particularly focusing on the CP.
To offer clearer proof, a visualization evaluation of the ingredient distribution of CP and its interplay with OAA1 all through the degradation course of was performed (Fig. 3f). In purified PC, carbon and oxygen have been uniformly distributed throughout the intact protein floor. Following the addition of OAA1, particular enrichment of C and Cu on the CP floor was noticed, whereas oxygen remained uniformly distributed all through the sector of view, with no important degradation of CP at this stage. The following addition of hint quantities of H2O2 led to protein degradation into fragments. At this level, Cu turned freely distributed after shedding its CP goal, and it’s noteworthy that oxygen was closely adsorbed on the residual protein fragments, alleged to be produced by ·OH and their involvement within the degradation response. The introduction of OAA1 confirmed the co-localization of C and Cu with CP, substantiating the particular binding affinity of OAA1 to CP and thereby its function in facilitating the environment friendly subsequent degradation of CP.
In a dwelling plant mannequin, the invasion of plant viruses induces stress responses, resulting in a major improve in ROS ranges in contaminated tissues [54, 55]. Nonetheless, the H2O2 produced (in contrast with the NC 5.58 instances) by crops alone is inadequate to trigger virus lysis, as confirmed by our experimental outcomes (Determine S29a, b). Though earlier research have demonstrated that H2O2 serves as a wonderful precursor for ·OH in animal illnesses [56, 57], its software in crops has been much less reported. ·OH, generated by the Fenton/Fenton-like response which depends on H2O2, is able to inflicting extreme injury on proteins and nucleic acids [58]. Conversely, the absence of H2O2 in wholesome plant tissues signifies that OAA1 reveals excellent biocompatibility [59], making certain they don’t pose a menace to the proteins inside these tissues.
The precise binding of OAA1 to CP induces degradation of neighboring segments
The essential step in elucidating the degradation mechanism of CP by OAA1 was to accumulate an correct tertiary construction mannequin of CP. For the primary time, this examine resolved the three-dimensional construction of PMMoV CP utilizing cryo-electron microscopy, reaching a decision of two.91 Å with a B issue of − 63.8 Å (Fig. 4a–c, Determine S30). In vitro, the free CP assembles into disk-shaped constructions, and our constructed self-assembled disk construction includes 17 CP protein monomers, displaying C17 symmetry. Every CP measures 70.4 Å in size, 37.5 Å in width, and 26.3 Å in top (Determine S31), composed of 4 main helices and two minor helices, together with two distinct β folds (Fig. 4c). The cryo-electron microscopy construction reveals variations when in comparison with its intently associated tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) [60].
Development of the CP degradation mannequin. a Prime and facet views of CP cryo-EM photographs and development of a high-resolution mannequin. b Gold-standard Fourier shell correlation (FSC) signifies an total decision of two.91 Å. c Three-dimensional structural mannequin of the PMMoV CP monomer, distribution of three-dimensional electrostatic potential of CP, three-dimensional hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity distribution. d TEM photographs depicting the CP degradation of OAA1 at completely different time factors and statistical evaluation of peptide sequences in OAA1 samples uncovered over numerous durations. e Particular degradation websites of OAA1 recognized throughout the first 15 min. The evaluation of the degradation course of was carried out utilizing three impartial replicate experiments
A time-dependent kinetic mannequin was developed to research the interplay between OAA1 and CP. Amino acid sequencing evaluation was performed on samples taken after 5, 10, and 15 min of co-incubation of OAA1 and CP for degradation. After 15 min, within the full-length sequence of 157 amino acids, protection within the management group reached 92.4%, whereas within the degradation remedy group, it averaged solely 57.3% (Fig. 4e). The precise sequences that might not be detected have been statistically recognized as 1-MAYTVTSANQLVYLGSVWADPLE-23 43-TTVQQQFSDVWK-54, 73-YNAVLDSLVSALLGAFDTRNR-93, and 147-SASGLTWATTP-157, positioned respectively at each ends and the center of the CP sequence. TEM imaging outcomes of the degradation course of depict a gradual breakdown over time, accompanied by a discount in peptide sequence content material because the incubation time progresses (Fig. 4d). Moreover, the abundance of most sequences reveals a gradient variation with degradation time (Determine S32).
The unfinished protection within the management group was attributed to the quick sequences produced by protease hydrolysis, which have been undetectable within the evaluation [61, 62]. Conversely, the lacking amino acid fragments within the remedy group have been longer segments that remained undetectable as a consequence of materials degradation [63, 64]. Earlier research have proven that chiral nanomaterials can degrade particular sequences of the CP of TMV by way of a hydrolysis course of, probably impartial of the sturdy oxidative stress induced by free radicals [34]. Nonetheless, our findings point out that OAA1 reveals sustainable degradation exercise, suggesting that long-term publicity could result in the whole degradation of all sequences. Nonetheless, it was noticed that the degradation course of initiates from particular sequences, as evidenced by the absence of solely three sequences, 1-MAYTVTSANQLVYLGSVWADPLE-23, 73-YNAVLDSLVSALLGAFDTRNR-93, and 147-SASGLTWATTP-157, at each 5 and 10 min. By 15 min, the absence of the 43-TTVQQQFSDVWK-54 sequence had elevated, together with a notable lower within the abundance of peptide fragments. Thus, these degradation processes could finally obtain completion over time.
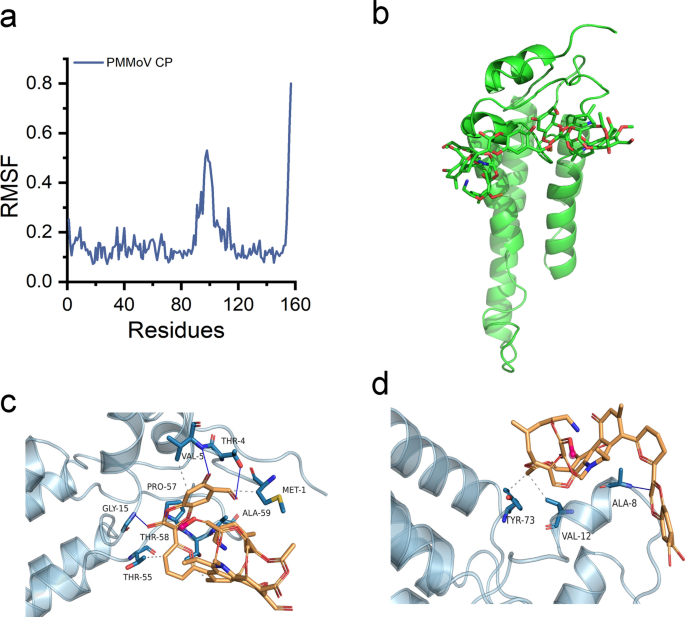
To discover the soundness and kinetic traits of the OAA1/CP advanced in aqueous resolution, modeling of the composition and content material of OAA1 components was performed, adopted by subsequent optimization to derive a simplified unit mannequin of OAA1 (Determine S33). The Root Imply Sq. Deviation (RMSD) of the system was examined, revealing speedy attainment of stability shortly after simulation initiation. Notably, the RMSD values of the protein exhibited minimal fluctuation all through the simulation (Determine S34a). Concurrently, the radius of gyration (Rg) remained constant (Determine S34b), indicating negligible alterations within the protein’s secondary construction all through the simulation. Evaluation of the solvent-accessible floor space (SASA) indicated a slight discount from 0 to 600 ns within the protein-small molecule system (Determine S34c). Delving deeper into amino acid dynamics through Root Imply Sq. Fluctuation (RMSF) evaluation, pronounced fluctuations have been noticed inside residues 90–120, juxtaposed with minor oscillations in different areas, suggesting stabilization presumably facilitated by interactions with the OAA1 (Fig. 5a). Moreover, hydrogen bond calculations between the protein and small molecule revealed various bond counts starting from 0 to six over the simulation interval (Determine S34d), underscoring the dynamic nature of their interplay.
Molecular dynamics simulation outcomes and interplay mode schematic. a RMSF plot displaying fluctuations of the advanced throughout simulation. b Total schematic illustration. c, d Native evaluation schematics. Proteins are illustrated in cartoon model, whereas small molecules are represented as sticks. Dashed traces point out hydrophobic interactions, and strong blue traces point out hydrogen bonds
Determine 5 supplies an in depth depiction of the contact modes noticed throughout the simulation course of. It’s illustrated that two small molecules adhere to particular areas of the protein, together with the α-helix and loop areas (MET1 ~ GLU23) in addition to central α-helix area (THR43 ~ LYS54) (Fig. 5b, Determine S35a). The vast majority of noticed binding modes contain particular person interactions between every materials and the protein, as depicted in Fig. 5c, d. This delineation highlights the hydrophobic interactions established between the small molecule and protein residues MET1, VAL5, THR55, and THR58. Moreover, hydrogen bonds are fashioned with THR4, VAL5, GLY15, PRO57, and ALA59, with bond distances starting from 0.329 nm to 0.306 nm (Fig. 5c). Determine 5d showcases the hydrophobic interplay between VAL12 and TYR73 (Determine S35c), accompanied by a hydrogen bond with ALA8 at a distance of 0.293 nm (Determine S35b). Consequently, the evaluation means that the binding of OAA1 with CP primarily serves as an anchoring operate, with the excessive biocompatibility of OAA1 materials posing no disruption to the binding website of CP. Following binding, degradation of close by websites is facilitated by way of the cooperative induction of hydroxyl radicals by H2O2.
When a nanomaterial enters a physiological surroundings, it quickly adsorbs proteins, forming what is named the protein ‘corona’ [65]. This examine means that the small-sized OAA1 probably interacts with the protein floor by way of an inverted mannequin, i.e., adsorbing OAA1 onto the protein floor. Molecular dynamics simulations evaluation signifies that OAA1 interacts with particular areas of the protein, specifically sequences 1–23 and 43–54, through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. Nonetheless, sequences 73–93 and 147–157 don’t exhibit direct contact with OAA1, however are nonetheless fully degraded. Therefore, the degradation noticed will be ascribed to the presence of free radicals in neighboring areas, notably ·OH, throughout the system.
Broad-spectrum exercise of OAA1 towards plant viruses
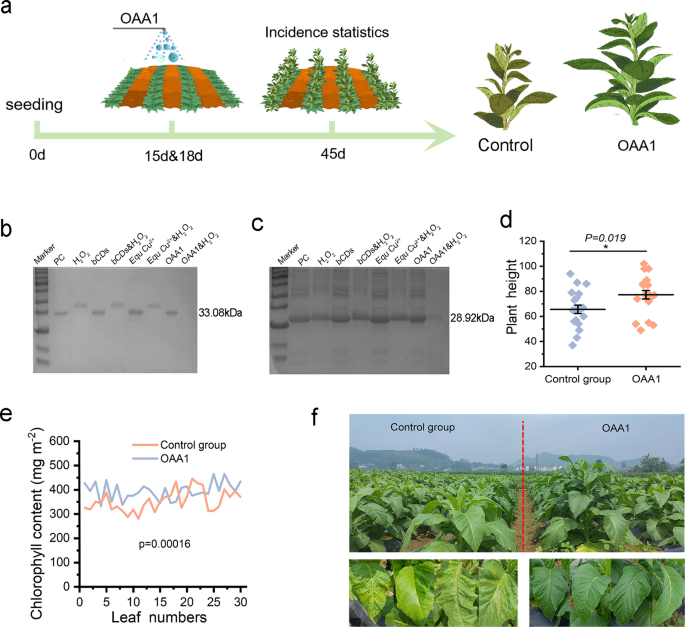
To additional affirm the broad-spectrum degradation exercise of OAA1, papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) (Fig. 6b) and tomato noticed wilt virus (TSWV) (Fig. 6c) have been used for verification, the co-incubation of OAA1&H2O2 with viruses CP resulted within the full degradation of CP. Below subject circumstances, the tobacco seedlings have been sprayed with OAA1 15 and 18 days after planting, respectively. Because of the appropriate local weather and vulnerable varieties, plant viruses contaminated quickly and the leaves exhibit a variety of pathological circumstances in management (water) remedies (Fig. 6a, f, Determine S36). Against this, the OAA1 exhibited the promoted impact on plant top and chlorophyll (Fig. 6d, e). These outcomes point out that OAA1 not solely demonstrates distinctive CP degradation exercise towards PMMoV in laboratory settings but additionally reveals important inhibitory results towards quite a lot of unknown plant viruses in subject experiments.
The broad-spectrum antiviral exercise of OAA1. a The scheme illustrated the timeline of progress of subject grown tobacco beneath OAA1 publicity (b) Degradation effectivity of PRSV CP following purification with OAA1. c Degradation effectivity of TSWV CP following purification with OAA1. d, e Response of chlorophyll content material and plant top to OAA1 publicity in subject experiments. f Development phenotypes of the OAA1-exposed group and the management group in subject circumstances